The Role Of Extensive Green Roofs In Sustainable Development

The role of extensive green roofs in sustainable development.
The role of extensive green roofs in sustainable development. A green roof s plants remove air particulates produce oxygen and provide shade. Therefore many countries are giving incentives to the house owners for the application of green roof. Before human development began dis turbing natural habitats soil and vegetation constituted part of a balanced ecosystem that managed precipitation and solar energy ef fectively. Green roofs contribute to the sustainability efforts of an organization through.
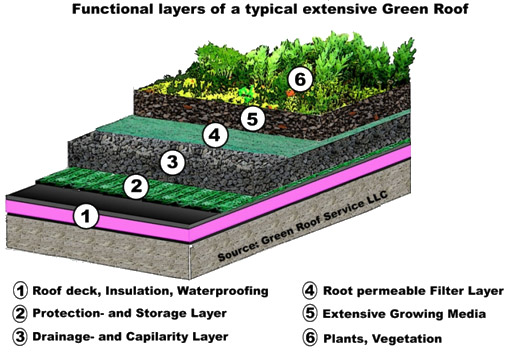
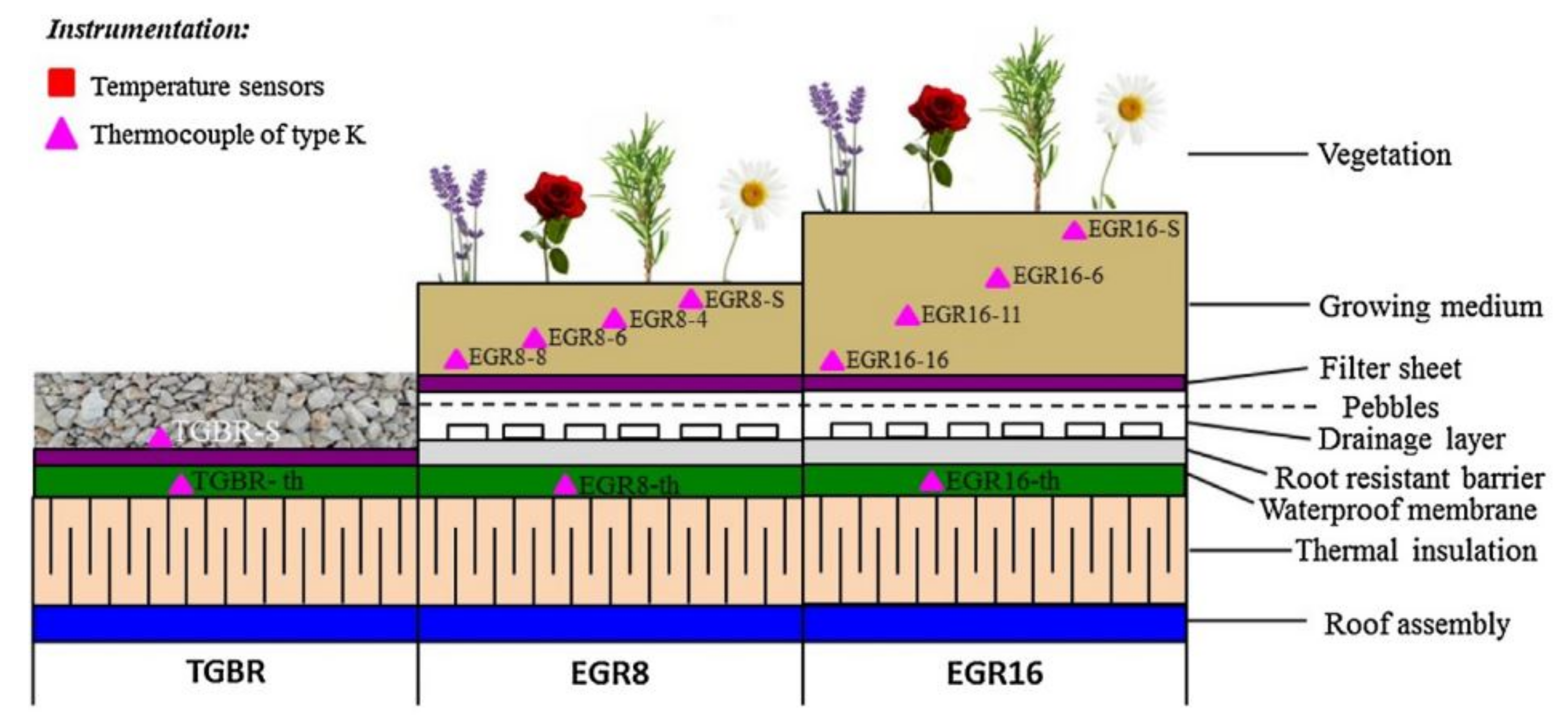
So if the roofs are made green by vegetating it will act a major role in mitigating the uhi effect. Green roofs are lightweight engineered rooftops designed to promote the growth of vegetation while protecting the structural integrity of the roof. Environmental and human health benefits of green roofs include air purification urban heat island amelioration lower building energy costs increased urban biodiversity reduced stormwater runoff and improved stream water quality. Therefore the focus of this review is primarily on extensive green roofs.
This also improves the service life of hvac systems due to decreased usage. Extensive roofs are much more common than deeper intensive roofs. Additionally this natural protection against extreme heat enables green roofs to last twice as long as traditional rooftops. This can play a role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and adapting urban areas to a future climate with warmer summers.
Green roofs absorb heat and filter the air keeping the temperature low getter 2006. In addition green roofs play a critical role in improving the urban environment by enriching the biodiversity delaying the storm peak to the drainage system diminishing the runoff quantity purifying the air pollutants as well as the runoff quality. The benefits of green roof show that it plays an important role in making cities safe sustainable and resilient to climate change. In natural areas much of the rain.
The technology addresses a wide array of environmental issues associated with urbanization. Conserving energy by insulating the building and mitigating thermal heat gain which reduces the need for heating and cooling.