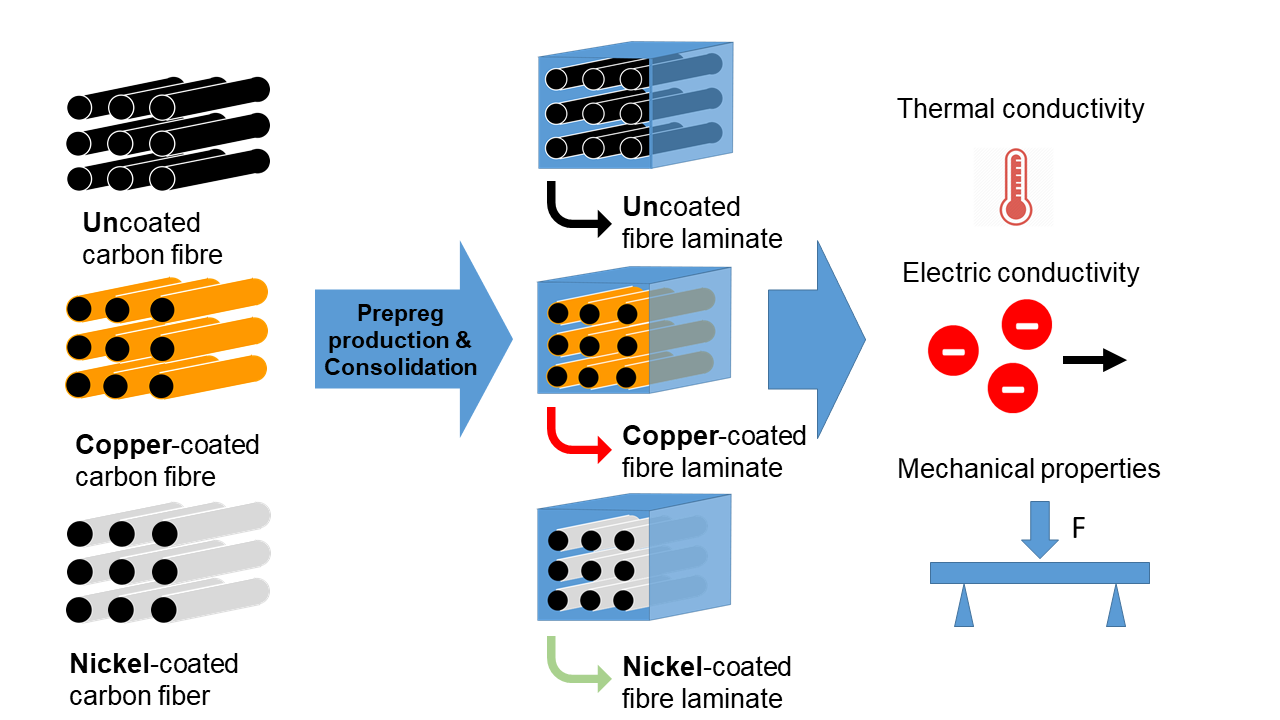
Thermal Conductivity Carbon Fiber Laminate

The thermal conductivity of a sample with laminate plys in the configuration 45 90 0 3 90 45 has also been measured.
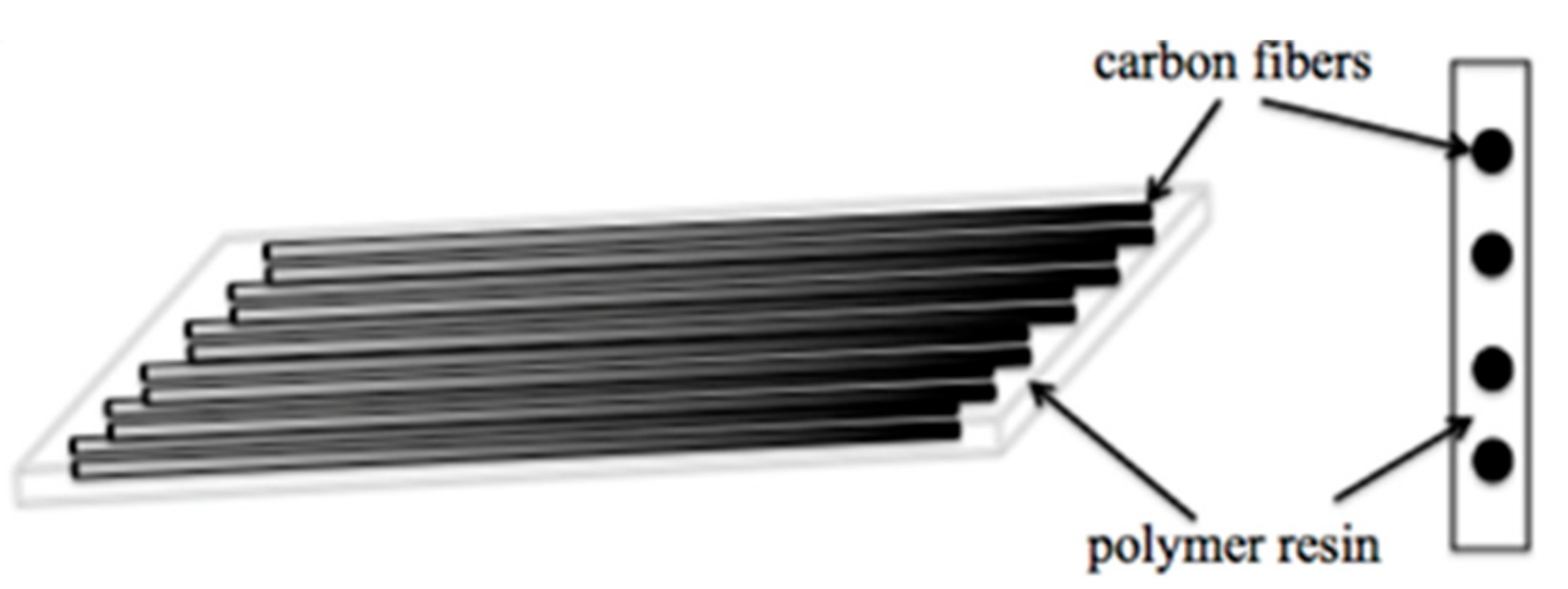
Thermal conductivity carbon fiber laminate. Starting with thermal conductivity components for the individual continuous unidirectional fiber reinforced lamina or ply a method has been developed to determine global conductivities in a laminated carbon carbon composite. Incorporating multi walled carbon nanotubes into cfrp composites is more advantageous for improving electrical conductivity whereas incorporating gnps is more beneficial for enhancing thermal conductivity. Assuming that all laminae are identical in thickness and in fiber content effective thermal conductivity in each global direction is determined for the laminated composite. However the thermal conductivities of these cfrp materials are generally poor due to low axial thermal conductivity of pan based carbon fiber which greatly limits their application in the satellite structure panels.
For the multidirectional sample the thermal conductivity ranges from 0 22 w mk at 5 7 k to 2 98 w mk. The in plane thermal conductivity of cfrp is expected to attain to 120 w m k thermal conductivity of 2024 t3 aluminum alloys is about 120 w m k in the satellite structure. At room temperature the thermal conductivity in the 0 direction is 7 times that in the 90 direction. Emissivity and thermal conductivity of carbon fiber epoxy laminates were characterized beforehand.
A bi experiment inverse method combining fe modeling and steady state temperature measurements on a heated test piece was used to characterize the thermal conductivity. On the one hand these carbonaceous fillers possess high thermal conductivity which act as functional component to enhance the thermal conductivity of composite laminate. Infrared image analysis was used to determine the emissivity of the composite.