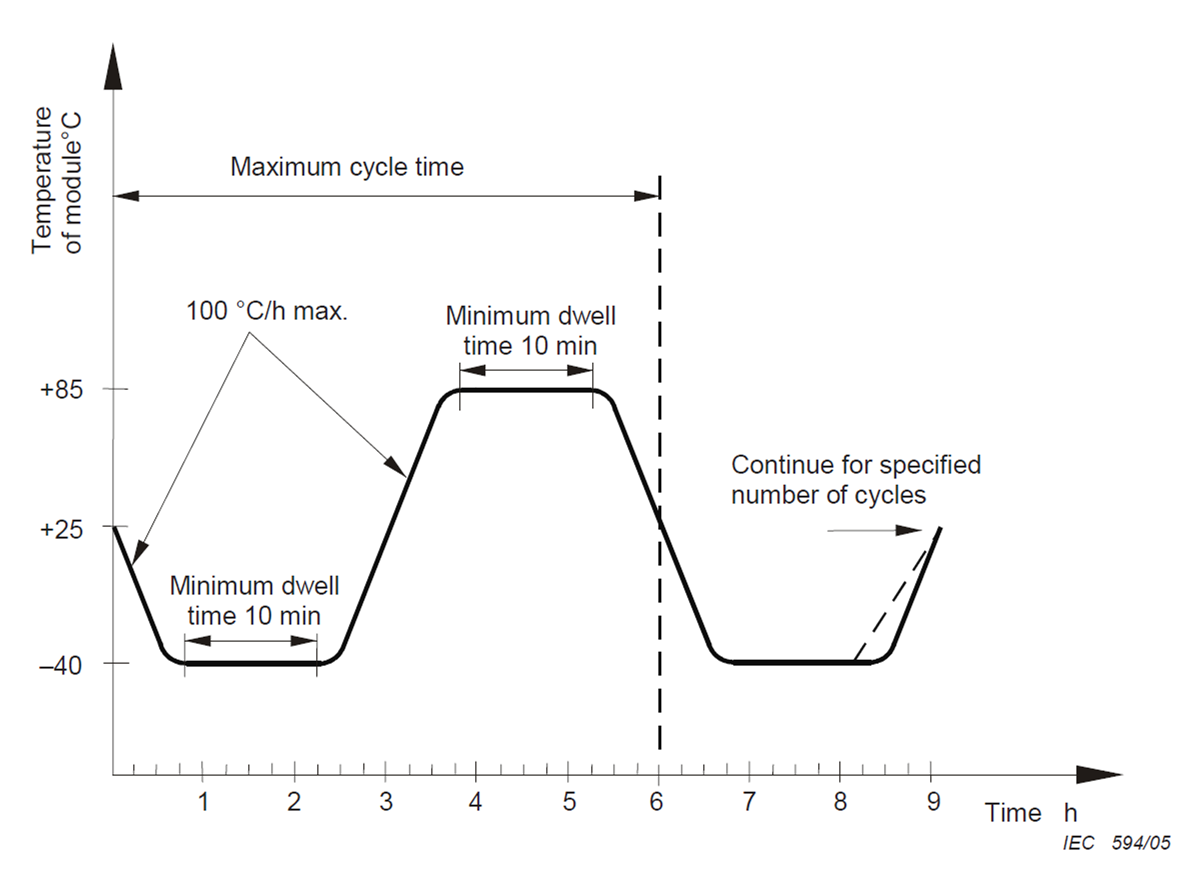
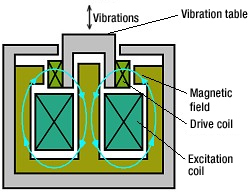
Thermal Cycling Test Procedure

Ovens are limited in speed and high end temperature.
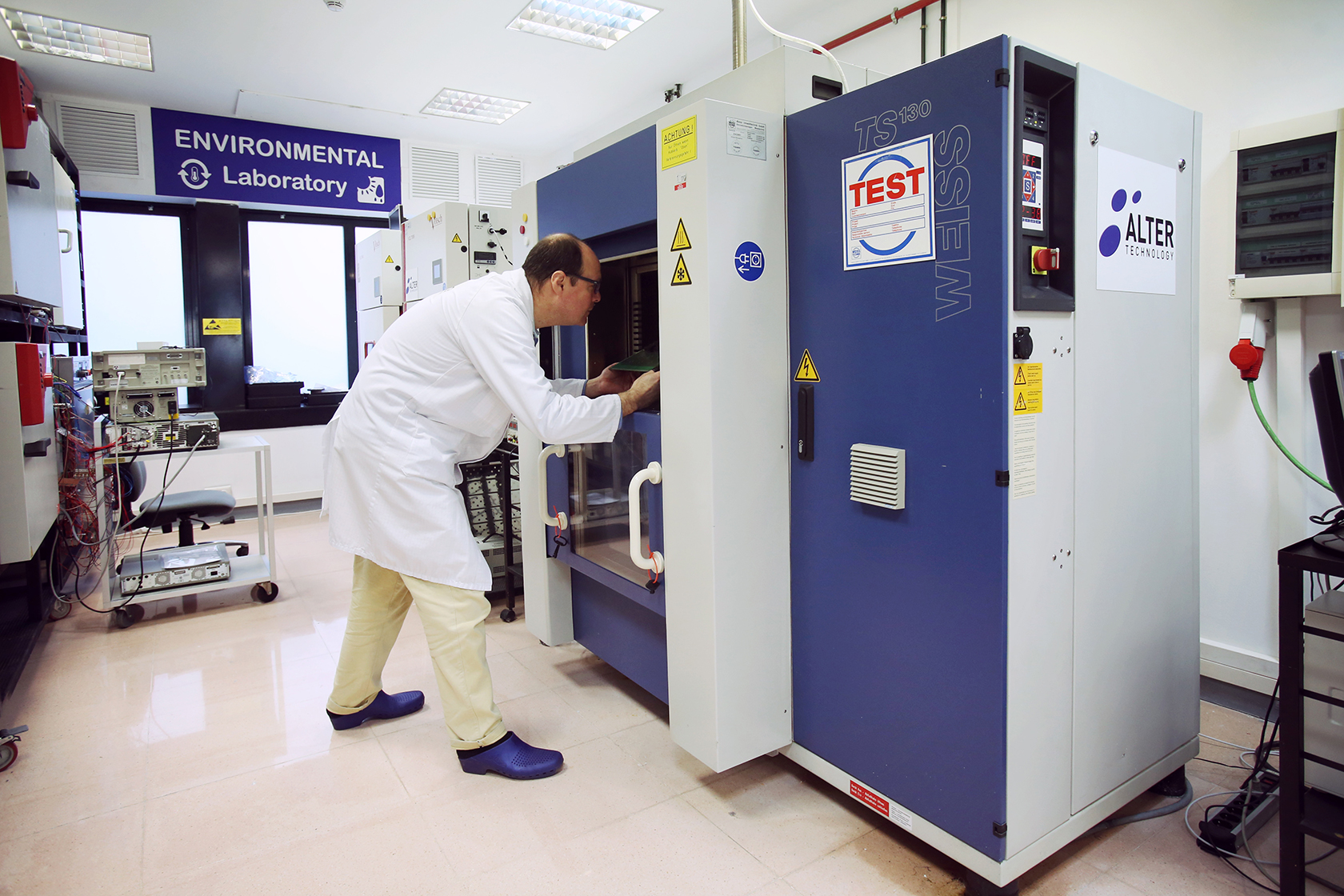
Thermal cycling test procedure. Thermal cycling test can verify the quality of design of the parts raw materials manufacturing procedure and installation process. It involves exposing test subjects to a controlled cycle of varied periods of hot cold and wet dry. Thermal cycling ovens are capable of achieving temperature ranges between 60 and 140 c. The length of exposure time and environmental extremes depend entirely on the type of product and its intended application.
Thermal cycling is another term often associated with performing temperature and humidity testing. Thermal cycling is the test or process of cycling a material or device through two set temperature extremes usually at a somewhat high rate of change of temperature. Thermal cycling testing assures your equipment meets the necessary standards. It is defined as an environmental stress test used to evaluate the reliability of the material or the product and to identify any manufacturing defects early by inducing failure.
It should be noted that temperature cycling may also be referred to as thermal cycling or thermal shock testing. The thermal cycling profile will replicate the same path to failure as seen in normal use. To conduct the test all parts of the piping system will be involved such as pipes fittings joints and welds. 5 1 exposing a specimen to conditions of one directional environmental cycling can increase its moisture content until a decrease in material properties occurs at a specific number of cycles.
This very brief introduction to thermal cycling and the ways it can damage your product implies that you must understand the specific failure mechanisms before designing your thermal cycling based life test. Thermal cycling test is the most important performance test for hot and cold water piping system. Such a test could be inappropriate due to the number of cycles required to cause a decrease in material properties since product performance issues often arise only after many years of exposure. However some test standards such as mil std 883 make the distinction between temperature cycling being performed as air to air testing and thermal shock being performed with the samples transferred between liquids.
The transition between temperature extremes occurs very rapidly during thermal shock testing greater than 15 c per minute. Also called a heat dunk test the thermal cycling test procedure heats the assembly to 180 degrees celsius and then immediately dunks it into water. Thermal shock testing also called temperature shock testing or temperature cycling exposes products to alternating low and high air temperatures to accelerate failures caused by repeated temperature variations during normal use conditions.




































.jpg)






