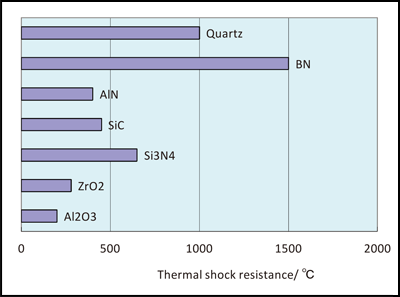
Thermal Shock Resistance Polymers Vs Ceramics

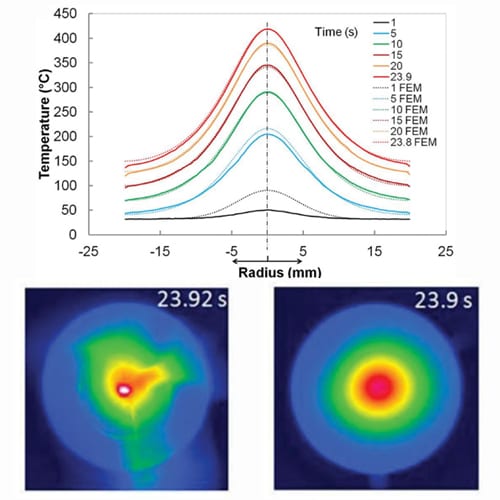
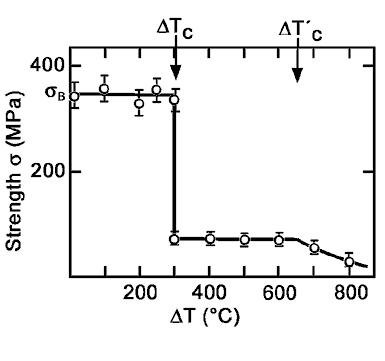
This is a process that takes place abruptly when there is a sudden variation of temperature either from hot to cold or vice versa.
Thermal shock resistance polymers vs ceramics. Asked jul 25 2020. Density ductility hardness corrosion resistance hardness thermal conductivity electrical conductivity wear resistance. Compare metals polymers and ceramics on a chart or table using the following properties and the ratings low high and highest. The composition of coating materials and the spraying conditions are shown in table 1 the ni 21cr 10al 0 8y wt alloy was plasma sprayed to a thickness of 100μm before the spraying of.
Some ceramic fillers are characterized as thermal shock resistant apparently surviving temperatures as high as 1400 c. Microsize such particles were put into a thermoplastic vulcanizate tpv namely blends of polypropylene pp and ethylene propylene diene epdm rubber at the concentration of 5 wt. A stainless steel specimens jis sus304 for the thermal shock test 30 450 13mm and for the hot corrosion test 50 50 5mm were sprayed with a metallic undercoat and ceramic top coat in a double layer. Thermal shock is a variation in temperature which causes tension in a material.
It frequently causes breakage in the material and is most common in brittle materials such as ceramics. It can be also extended to the case of a thermal gradient which makes different parts of an object expand by different amounts.




























.jpg)














