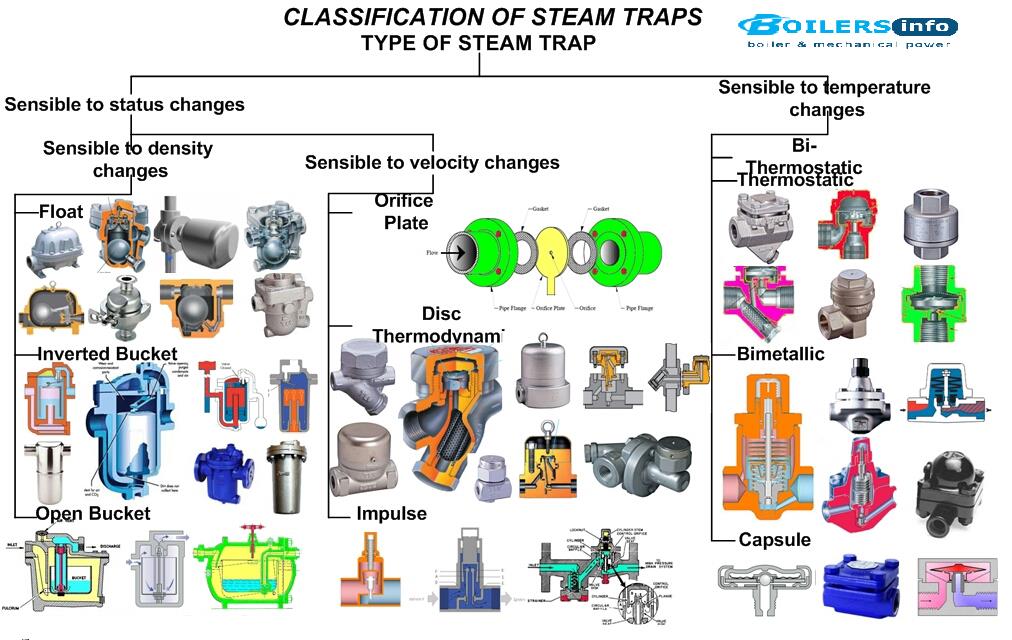
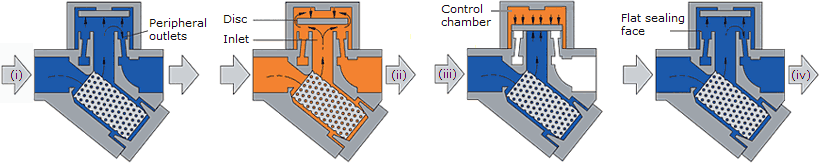
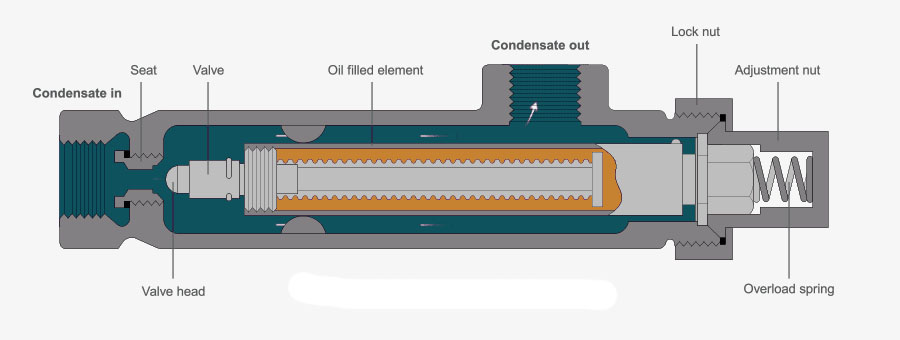
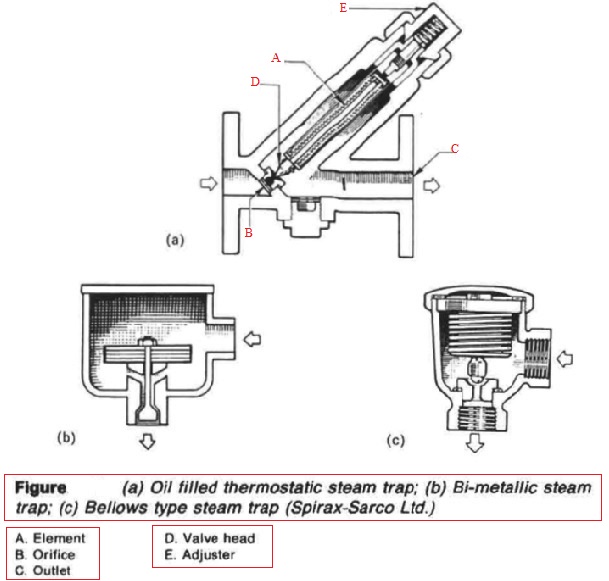
Thermostatic Steam Trap Working Principle

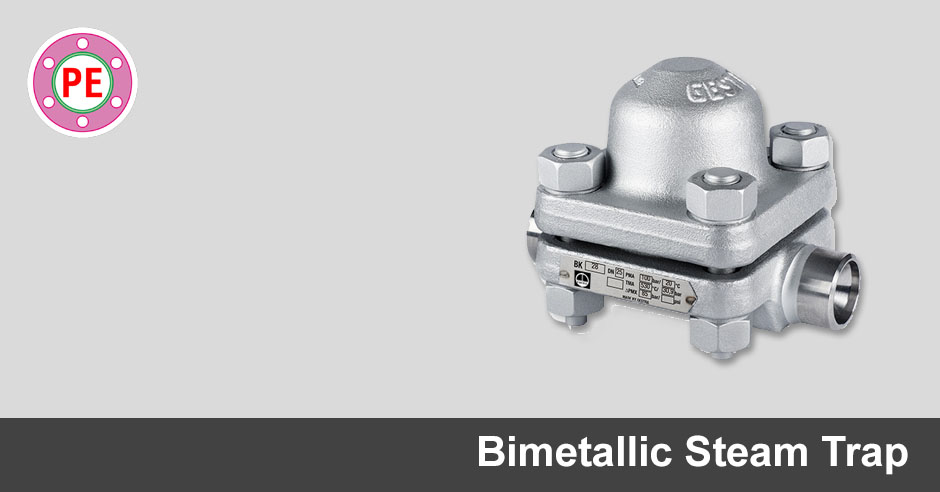
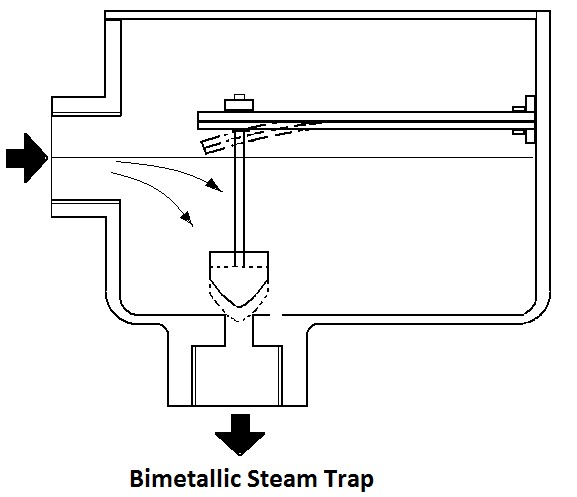
It utilizes bimetallic strips of dissimilar metals stacked together in pairs.
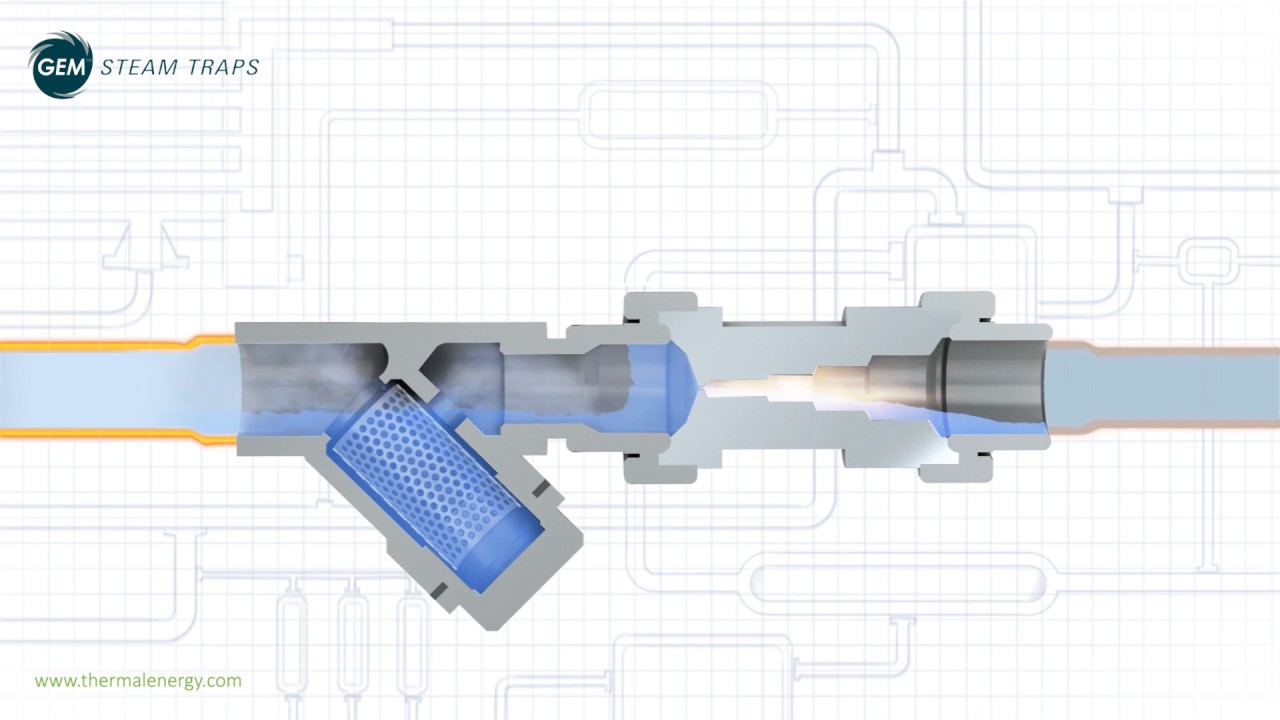
Thermostatic steam trap working principle. As its name implies the mechanism consists of an inverted bucket which is attached by a lever to a valve. This video explains how a thermodynamic steam trap works. Discharge condensate as soon as it is formed unless it is desirable to use the sensible heat of the liquid condensate. The expansion of element a leads.
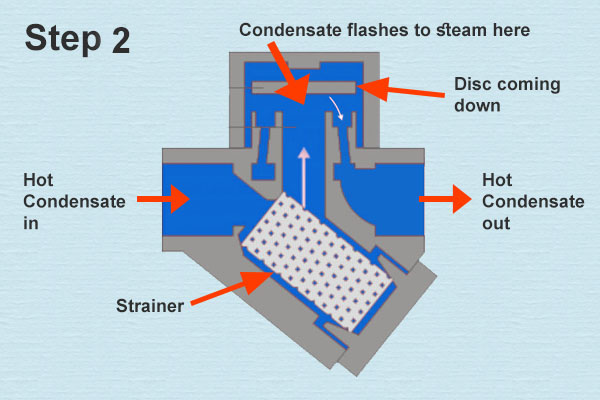
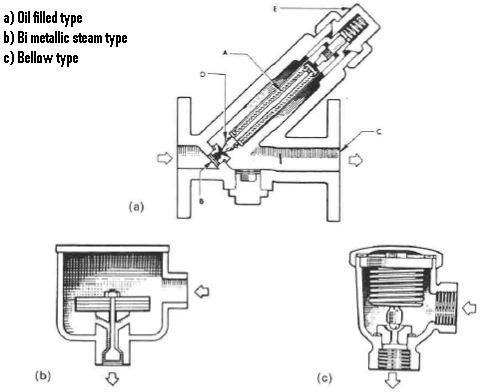
Working principle of bimetallic steam trap. An essential part of the trap is the small air vent hole in the top of the bucket. In an oil filled element type steam trap as shown in the figure the element a expands as the temperature of the condensate rises. A steam trap is a device used to discharge condensates and non condensable gases with a negligible consumption or loss of live steam steam traps are nothing more than automatic valves they open close or modulate automatically.
Each operates in a different way and is suited to specific types of application. In this article we will learn about thermodynamic and vacuum traps. At star up air will enter the steam trap and will be discharged out through the bleed hole. The three important functions of steam traps are.
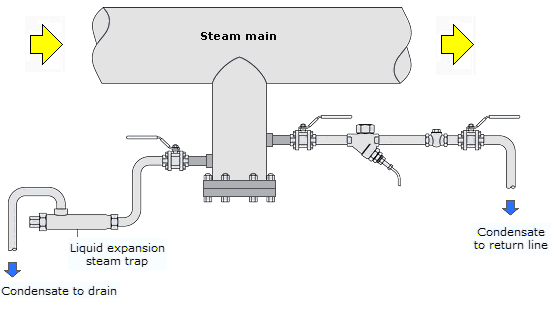
Thermoliquid bimetal thermowax. The inverted bucket steam trap is shown in figure 11 3 3. Thermostatic traps operate in response to the surrounding steam temperature. Inverted bucket steam trap.
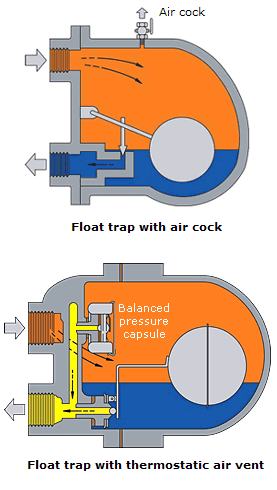
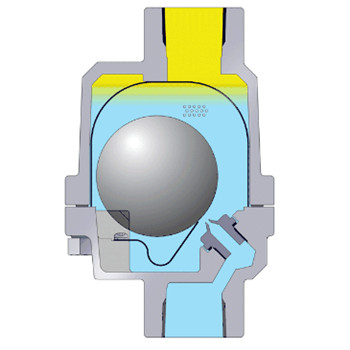
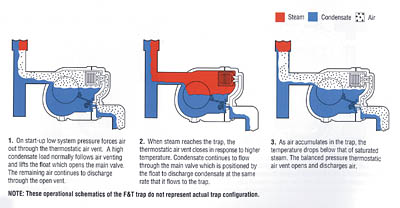
These are mechanical type of steam traps working on the principle of buoyancy. The operation principle for thermostatic steam traps utilizes the temperature difference between steam and condensate. The operation and benefits of 3 different types are considered here liquid expansion traps bimetallic and balanced pressure thermostatic traps. Tlv traps offer three types of temperature sensing materials to detect differences in temperature.
Initially the bucket is resting at the bottom of the steam trap and the valve seat is wide open. Thermostatic trap also known as the temperature trap uses expansion of a bimetallic strip an oil filled element or a flexible below to activate a valve.