Time Period Of A Satellite Revolving In An Orbit Of Radius R Is Such That

From the second postulate of bohr s theory.
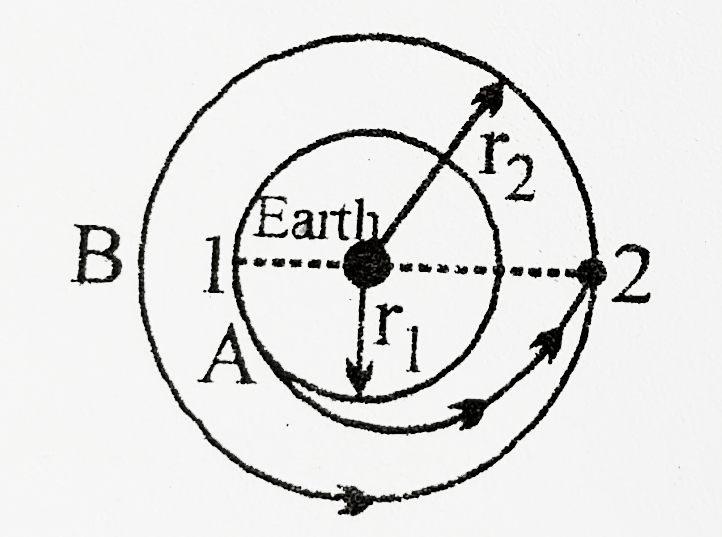
Time period of a satellite revolving in an orbit of radius r is such that. It moves around the earth once in 27 3 days in an approximate circular orbit of radius 3 85 10 5 km. The time period of another satellite revolving in the circular orbit of 2584283. Time required for a satellite to complete one orbit orbital speed speed of a satellite in a circular orbit. This can be easily analysed and solved with the help of kepler s law of planetary motion.
Radius of earth 6 37 x 10 6 m. Since ε o h π m e are constant r n. According to the law the squares of the sidereal period of revolution of the planets are directly proportional to the cube of the mean distance from the. Given g 9 81 m s 2.
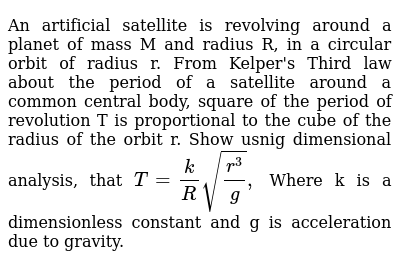
The time period of a satellite revolving in a circular orbit of radius r is t. The difference between the final initial total energies is. A body moving in an orbit around a planet is called satellite. Calculate the radius of such an orbit based on the data for earth in astronomical data.
Thus the radius of the bohr s orbit of an atom is directly proportional to the square of the principal quantum number. A body of mass m is moving in a circular orbit of radius r about a planet of mass m. At some instant it splits into two equal masses. The period of the earth as it travels around the sun is one year.
Find its period of revolution. The expression for velocity of electron in bohr s orbit. The moon is the natural satellite of the earth. The first artificial satellite sputnik was launched in 1956.
For this purpose the angle variable is unrestricted and can increase indefinitely as the particle revolves around the central point multiple times. The first mass moves in a circular orbit of radius 2 r and the other mass in a circular orbit of radius 2 3 r. This is the required expression for the radius of bohr s orbit. If you know the satellite s speed and the radius at which it orbits you can figure out its period.
The period of a satellite is the time it takes it to make one full orbit around an object. If g r 3 instead of r 3 1 then the relation between time period of a satellite near earth s surface and radius r will be view answer a satellite is revolving in a circular equatorial orbit of radius r 2 1 0 4 km from east to west. In what direction is such a satellite projected and why must it be in the equatorial plane. What is the possible use of such a satellite.
It can be also be used for the instantaneous speed for noncircular orbits in which the speed is not constant. You can calculate the speed of a satellite around an object using the equation.